In the world of hot water systems, the efficiency and effectiveness of a heat pump are significantly influenced by its refrigerant. At HiTech Hot Water, we understand the pivotal role played by refrigerants in heat pump technology. This article aims to demystify what refrigerants are and their importance in hot water heat pumps.
Definition and Working Principle
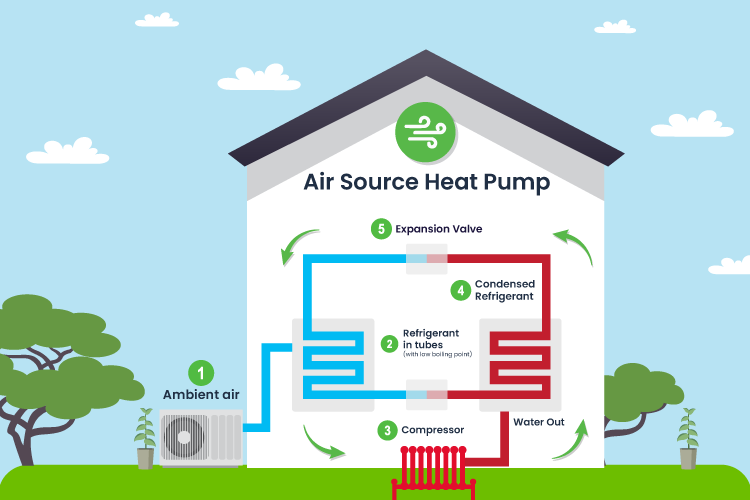
In the context of heat pump technology, the heat pump refrigerant is an essential substance used for absorbing and releasing heat. Integral to the function of both heat pumps and refrigeration systems, this heat pump refrigerant undergoes a cycle where it evaporates at lower temperatures and condenses at higher ones.
This cyclical process is crucial in heat pump hot water systems, enabling the refrigerant to efficiently extract heat from the ambient air and utilize it for water heating purposes. This operation of the heat pump refrigerant is a cornerstone in the effective working of heat pump systems.
Types of Heat Pump Refrigerants
The types of refrigerants commonly used in heat pump systems are diverse, each with specific characteristics. These include R-410A, R134A, R407C, R32, R1234ZE, R290, and R744.
Each of these refrigerants has unique properties that determine their suitability for different heat pump applications. Factors influencing their selection include environmental impact, efficiency, and compatibility with various system designs.
The choice of the right refrigerant is crucial in ensuring optimal performance and adherence to environmental standards in heat pump systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of using refrigerants in heat pumps include high efficiency in heat transfer, low boiling points, and non-toxicity in some types. However, some refrigerants have disadvantages like global warming potential (GWP) and ozone depletion potential (ODP), prompting a shift towards more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Advantages:
- High Efficiency: Refrigerants are key to the high efficiency of heat pumps, enabling effective heat transfer from one environment to another.
- Low Boiling Points: Their low boiling points allow refrigerants to vaporize and condense effectively at various temperatures, crucial for heat pump operation.
- Non-Toxicity: Some modern refrigerants are non-toxic, reducing health risks in case of leaks.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Advances in technology have led to the development of eco-friendly refrigerants with lower environmental impacts.
- Versatility: Different types of refrigerants cater to various heat pump designs and climatic conditions, enhancing flexibility in application.
Disadvantages:
- Global Warming Potential (GWP): Some traditional refrigerants have high GWP, contributing to climate change.
- Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP): Certain older refrigerants can deplete the ozone layer, leading to environmental concerns.
- Regulatory Changes: The refrigerant industry faces constant changes in regulations, affecting the choice and use of refrigerants.
- Cost and Availability: Eco-friendly refrigerants can be more expensive and less readily available than traditional ones.
- Compatibility Issues: Some refrigerants may not be compatible with older heat pump systems, necessitating upgrades or replacements.
Major Refrigerant Used in Heat Pump Hot Water
In our range of heat pumps at HiTech Hot Water, like the Emerald 200L Split Heat Pump and the Emerald 270L all-in-one heat pump, we use refrigerants that offer a balance of efficiency and environmental friendliness. These include newer, low-GWP refrigerants that meet modern environmental standards.
Refrigerant in All in One and Split System Heat Pumps
In all-in-one and split system heat pumps, the selection of refrigerant is determined by the specific model and its design requirements. With an emphasis on the heat pump and refrigeration efficiency, split systems often use different refrigerants than all-in-one units due to their unique design characteristics.
At HiTech Hot Water, we ensure that our heat pump and refrigeration systems are equipped with refrigerants that not only adhere to strict environmental regulations but also maximize operational efficiency. This careful selection is pivotal in delivering high-performance heat pump solutions.
How to Check Refrigerant in Heat Pumps
Checking the refrigerant in a heat pump system usually requires technical expertise. It involves examining the refrigerant lines for leaks, checking pressure levels, and ensuring the system is charged correctly. Regular maintenance by a professional can ensure the refrigerant level is optimal for efficient operation.
- Visual Inspection of Refrigerant Lines: Look for signs of damage or leaks in the refrigerant lines. This can include visible cracks, wear and tear, or oil residue, which can indicate a leak.
- Checking Pressure Levels: Using specialized gauges, check the pressure in the refrigerant lines. Incorrect pressure levels can indicate either an undercharged or overcharged system, both of which can affect efficiency.
- Leak Detection: Employ methods such as electronic leak detectors, UV dyes, or soap solution tests to identify any leaks in the system.
- Assessing the Thermostat and Temperature Controls: Ensure that the thermostat and temperature controls are functioning correctly and are in sync with the actual temperature of the output.
- Listening for Unusual Noises: Unusual noises in the system can indicate issues with the compressor or the refrigerant flow, which might suggest a refrigerant problem.
- Professional Evaluation of Refrigerant Type and Level: A certified technician can assess the type of refrigerant used and whether the system has the correct amount, as both factors are crucial for optimal operation.
- Regular Maintenance Checks: Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure the system's refrigerant levels are always optimal, which can prevent future issues and maintain efficiency.
Comparison Between Refrigerants
When comparing the specific types of refrigerants used in heat pump systems, such as R-410A, R134A, R407C, R32, R1234ZE, R290, and R744, it's important to consider their distinct environmental impacts and efficiency levels.
These modern refrigerants have been developed to address the environmental concerns associated with older refrigerants like CFCs. For example, R-410A is known for its higher efficiency and lower ODP compared to older refrigerants.
R32 and R1234ZE, on the other hand, offer lower GWP, making them more environmentally friendly choices. Each refrigerant's efficiency in terms of heat transfer and compatibility with different system designs also plays a crucial role in determining its suitability for specific heat pump applications.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the refrigerant in a heat pump is a critical component that determines its efficiency and environmental impact. At HiTech Hot Water, we carefully select refrigerants for our heat pumps, balancing environmental considerations with the need for effective heating. Understanding the types, advantages, disadvantages, and methods of checking refrigerants can guide users in making informed decisions about their heat pump systems.